Smart lighting has emerged as one of the most popular and accessible smart home upgrades. From setting the mood to improving energy efficiency and security, intelligent lighting systems are changing how we interact with our environments. But beneath the surface of simple commands and color changes lies an advanced infrastructure. This article explores how smart home lighting works, revealing the layers of technology and design that make modern lighting intelligent and adaptable.
The Foundation of Smart Lighting
To understand smart lighting, it’s essential to recognize that traditional lighting only offers two states—on or off. Smart lighting, however, introduces flexibility, responsiveness, and connectivity. This shift is achieved by embedding wireless modules and processors into bulbs, switches, or fixtures, enabling them to receive signals and respond accordingly.
These components connect through networking protocols—such as Zigbee or Wi-Fi—that enable communication either through a central hub or directly with other devices. The goal is to create an ecosystem where lights respond to commands and environmental cues, offering both manual control and automated functionality.
Intelligence Through Automation
The defining feature of smart home lighting is automation. While remote control via an app or voice assistant is convenient, the real value lies in lights that react without the need for constant human input.
Imagine your living room lights turning on automatically at sunset, dimming gradually as you wind down for the evening. Or consider a hallway light that senses movement and activates briefly to guide your steps at night. These are simple automations, but they represent a significant enhancement in comfort and usability.
Such behaviors are configured using home automation software. Users can define rules based on time, activity, ambient light, or triggers from other devices. The lighting system becomes part of a larger web of interactions, adjusting in real time to changing conditions.
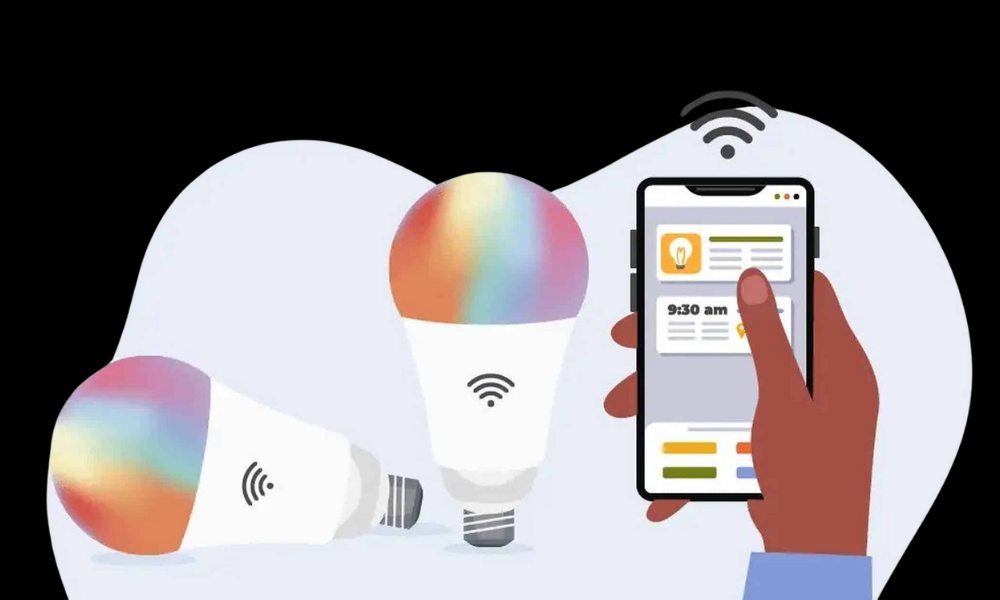

Device Communication and Ecosystem Integration
To enable this level of intelligence, devices must communicate smoothly. That’s where standards and protocols come in. Lights may talk directly to a hub, or in some systems, to each other in a mesh configuration. This setup improves reliability, especially in larger homes.
Integration is also crucial. Lighting rarely exists in isolation. In a connected home, lights can coordinate with window shades, climate systems, and media devices. A “bedtime” routine might lower the lights, adjust the temperature, and lock the doors—triggered with a single voice command or a tap on your phone.
In the background, the system constantly listens for triggers, evaluates conditions, and executes the appropriate commands. It’s a dynamic system that improves not just convenience, but energy efficiency and ambiance as well.
The Future of Smart Lighting
With growing adoption of universal protocols like Matter, the fragmentation that once defined smart lighting is starting to fade. Consumers are no longer tied to one brand or platform. As interoperability improves, setting up and expanding a smart lighting system becomes easier and more reliable.
Artificial intelligence is also beginning to shape the next phase of smart lighting. Systems can learn from user patterns, optimizing behaviors over time. Instead of programming every detail, users will be able to rely on adaptive lighting that understands context—when you’re working, relaxing, entertaining, or asleep.
When we ask how smart home lighting works, the answer lies in a combination of wireless communication, real-time automation, and responsive design. These systems are engineered to reduce friction, automate tasks, and make homes more intuitive. While the underlying technology is sophisticated, the experience is designed to be seamless. In the smart homes of today—and especially tomorrow—lighting is no longer passive. It’s active, adaptive, and entirely in tune with how we live.